Style leader from small beginnings
/Auburn made numerous pioneering contributions and was known for innovation, style and performance.
IN 1900, Frank and Morris Eckhart saw merit in making automobiles. With funding from their father, Charles, they established the Auburn Automobile Company that year.
The initial product was an assembled car built with parts sourced from an array of companies. The assembly process took place in a corner of the carriage company factory, whose craftsman built the wood framing for the bodies.
Nothing much came from their enterprise until the brothers displayed a car at the 1903 Chicago Auto Show. That put them into the spotlight.
By 1909 the brothers were successful enough to absorb two local automobile manufacturers and relocate production to a larger facility in 1909. The company enjoyed moderate and steady sales growth until the First World War, a shortage of materials dramatically curtailed manufacturing.
For investors and in media interviews the brothers painted a rosy picture, but the truth is that the company was in serious financial trouble. In 1919, on the cusp of bankruptcy, the company was sold to a group of Chicago investors that included William Wrigley Jr., the chewing gum mogul. Still, the company languished result of the economic recession, dated styling and a limited dealer network.
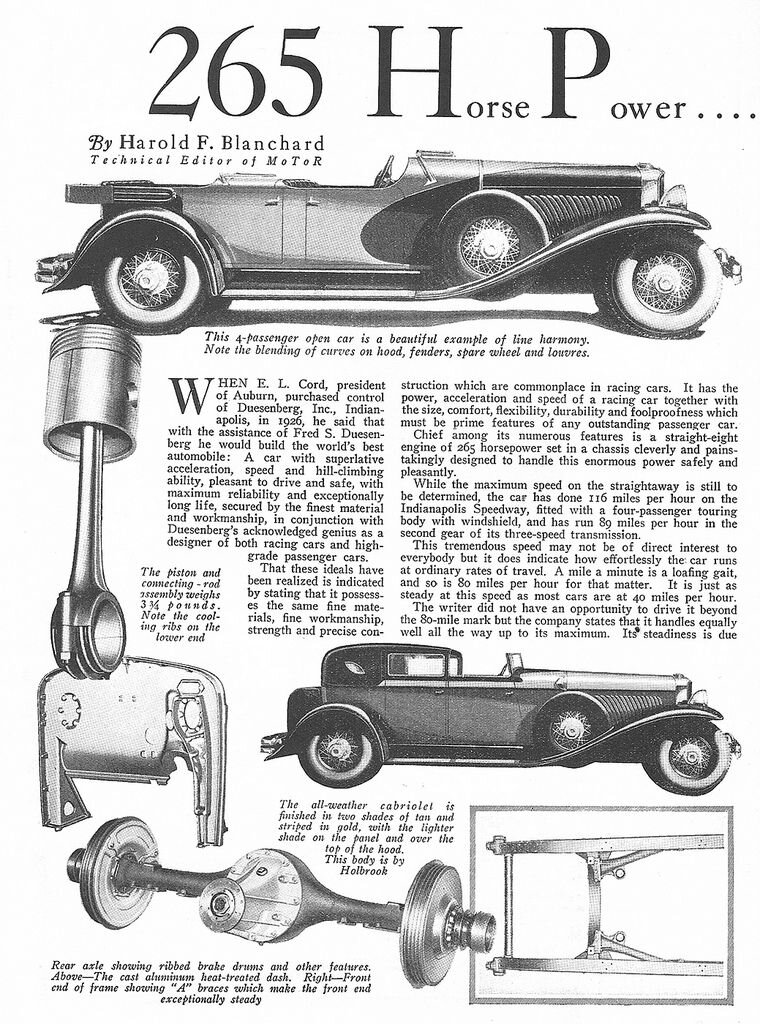
By 1924 only six cars a day were rolling from the factory and yet there was a surplus of unsold cars that was growing. Then to salvage something from their investment, the board of directors turned to E.L. Cord, the Chicago whiz kid that had transformed the St. Louis-based Moon from a moribund automobile manufacturing company to solvency.
After evaluating the operation Cord accepted the position of general manager at Auburn in exchange for a modest salary, stock options, and the option of buying controlling interest in the company.
His first step? Add nickel trim and repaint unsold stock. Then he cut the wholesale price but added an options list and hosted an auto show for area dealers on the town square.
He offered the dealers huge discounts and, within a few months, had sold off his overstock. As the log jam of unsold inventory began to move, in 1925 he contracted with Lycoming for eight-cylinder engines that were then installed in the formerly six-cylinder Auburns. This as well as a slight tweak to the bodies to present a more streamlined appearance and two-tone paint options led to a dramatic increase in sales.
Incredibly by 1926, Auburn was not only a profitable company, it was also counted among the top 20 manufacturers in the United States; no mean feat as there were dozens of automobile companies in operation at the time.
Rather than rest on his laurels, Cord hired Alen Leamy and Gordon Buehrig, cutting edge young automotive designers, and entered a limited partnership with the Duesenberg Company that had limited production of high-performance automobiles. He also established an extensive nationwide dealer network with a focus on select cities.
Cord used the Duesenberg association as the cornerstone for building a diverse industrial empire that included a new line of performance-oriented luxury cars. He incorporated some of these features into the L-29 Cord, the American automobile industry’s first successful front wheel drive car. Then with acquisition of controlling interest in Duesenberg, he shifted into high gear even though the economy was beginning to falter.
In 1928, the Auburn 8-115 was introduced with hydraulic rather than mechanical brakes. These cars were used to establish Auburn’s reputation for speed, performance, and luxury at the price of a Buick. At Daytona that year the Auburn 8-115 was driven to a speed record of 108.46 miles per hour.
The resultant media attention and a brilliant marketing strategy resulted in 1929 being the best year yet for the Auburn Automobile Company. Dealers clambered for cars and production was unable to meet demand even though manufacturing facilities were expanded.
Using the profitable company as leverage, Cord began acquiring companies to streamline operations, diversify income streams, and lessen the company’s dependence on other manufacturers. He purchased or acquired controlling interest in Stinson Aircraft, Anstead Engine Company, Lycoming, Limousine Auto Body, Duesenberg Motors, and Columbia Axle Company. He also expanded into the commercial market by introducing the Auburn Saf-T-Cab, a car purpose built as a taxi. This led to a limited partnership with Checker Cab Manufacturing Company.
Even thought the economic situation had deteriorated dramatically, and automobile sales had plummeted, in 1932 two new Auburns were introduced, the eight cylinder Model 8-100 and the astounding Model 12 series with V-12 engines at an incredible price of just $975 for the coupe. And as an option, a Columbia dual ratio rear axle was available. For promotion, a fully loaded Auburn Twelve Speedster set several speed records at Muroc Dry Lake, many of which stood until the late 1940s.
Even though sales and profits were plummeting precipitously at the end of 1932 the Auburn 851, a boat tail speedster designed by Gorden Beurig, with a Lycoming straight eight engine and a Schwitzer-Cummins supercharger was introduced. The car was sold with a written guarantee of 100 miles per hour and a plaque on the dash stating that the car had been tested to that speed by Indianapolis 500 driver Abe Jenkins. About 500 of these stunning Auburns were built and sold for $2,245. Still, the company lost money on each car sold as it had been conceived to get buyers into the showroom with the hope of selling them one of the cheaper Auburns. Initially the scheme was a success as sales of Auburn increased by 20 percent, but overall sales had declined by nearly 60 percent since 1929.
To stave off impending collapse, a six-cylinder model was introduced in 1935, initial development of a proposed diesel-powered limousine for 1936 was launched and production of the V-12 and the straight eight were cut. Then precious resources were diverted to the now legendary 810 and 810 Cords. As a result, the last Auburns rolled from the factory in 1936 with little fanfare.
Under investigation from the Securities and Exchange Commission, largely resultant of a questionable partnership with Checker Cab Manufacturing, and the Internal Revenue Service resultant of accounting practices, Cord sold his interest in Auburn-Cord-Duesenberg. On August 7, 1937, the Auburn Automobile Company went out of business and assets were liquidated. In the grand scheme of things, it was a small loss for Cord as at this time he was one of the richest men in the world. He owed airlines, aircraft companies, communication companies, ship lines, and other businesses including taxi franchises.
The Auburns that have survived into the modern era are treasured and revered. When equipped with the Columbia two speed axle, they blend modern road manners with classic car styling and luxury making them an ideal touring car for the modern enthusiast.
Written by Jim Hinckley